The Communication Networks (Las Redes de Comunicacion)1. IntroductionCommunication networks are nothing more than the possibility of a universal sharing of information between groups of computers and their users, a vital component of the information age. Widespread computer or personal computer (PC) and local area network (LAN) during the eighties has led to the ability to access information in remote databases, load applications from overseas points, send messages to other countries and share files, all from a personal computer. The networks that allow this are advanced and complex equipment. Its effectiveness is based on the confluence of many different components. The design and implementation of a global network of computers is a major 'technological miracles' of recent decades. 2. Concept Network It is a set of physical devices hardware and software "software", by which computers can communicate to share resources (disks, printers, software, etc..) And (time of calculation, data processing, etc.). . Each of the computers connected to the network is called a node. Network is considered local if it only reaches a few kilometers.
3. Types Of Networks Information networks can be classified by their size and topology. A small network can start to grow with the organization or institution. Below is the different types of networks available:
Extension According to geographical distribution: Network segment (subnet) :A network segment is usually defined by the hardware or a specific network address. For example, in the environment "Novell NetWare" on a network segment includes all workstations connected to a network interface card on a server and each segment has its own network address.
Local area network (LAN) :A LAN is a network segment that is connected workstations and servers or a set of interconnected network segments, usually within the same area. For example a building.
Campus Network A campus network is extended to other buildings within a campus or industrial area. The various segments or LAN in each building are connected by network cables support. Metropolitan area network (MAN) A MAN network is a network that spreads by towns or cities and are interconnected by various public or private facilities such as telephone system or the suppliers of microwave communication systems or optical media.
Wide Area Network (WAN and global networks) WANs and global networks extend beyond the borders of cities, towns or nations. The links are made public telecommunications facilities and private, in addition to microwaves and satellites.
4. Topology The topology or logical form of a network is defined as the way to build the cable to individual workstations, for walls, floors and ceilings of the building. There are a number of factors to consider to determine which topology is most appropriate for a given situation. There are three common topologies:
"Ring"The stations are linked to each other in a circle through a common wire (Figure 1). The last node of the chain is connected to the first closing the ring. The signals traveling in one direction around the circle, regenerating at each node. With this approach, each node examines the information that is sent through the ring. If information is not directed to the node that the review, go to the next in the ring. The disadvantage of the ring is that if a connection is broken, the entire network goes down. Figure 1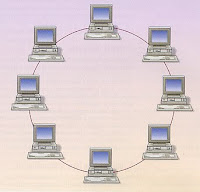
"Star"
The network joins a single point, usually with a centralized control panel, as a hub for wiring (Figure 2). The blocks of information are routed through central control panel to their destinations. This scheme has an advantage to have a control panel that monitors the traffic and avoid collisions and a broken connection does not affect the rest of the network.
Figure 2 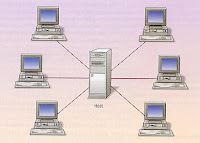
"Bus"
The stations are connected via a single cable segment (Figure 3). Unlike the ring, the bus is passive, there is no regeneration of signals at each node. The nodes in a network of "bus" transmit information and hope it will not collide with other information transmitted by another node. If this happens, each node waits a short amount of time at random, then tries to relay information. Figure 3
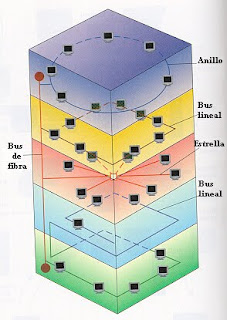
The linear bus, star and ring sometimes combine to form combinations of hybrid networks (Figure 4).
* Star Ring
This topology is used in order to facilitate network administration. Physically, the network is a central star in a hub, while logical level, the network is a ring.
* "Bus" star
The order is equal to the previous topology. In this case the network is a "bus" to be physically wired as a star through hubs.
* Hierarchical Star
This structure cabling is used in most existing local networks through hubs pair arranged in cascade form a hierarchical network.
Figura 4
5. Network Protocols
A network protocol is like a language for communication of information. Are the rules and procedures used on a network to communicate between nodes that access the cable system. The protocols govern two levels of communication:
The high-level protocols: These define the way applications communicate.
The low level protocols: These define how signals are transmitted by cable.
As usual in the case of computers constantly changing protocols are also constantly changing. Currently, the most commonly used protocols in the networks are Ethernet, Token Ring and ARCNET. Each of these is designed to provide some kind of network topology and have certain standard features.
Ethernet
Currently the protocol is easy and inexpensive. Use the topology of "Bus" linear.
Token Ring
The network protocol is the IBM token ring, which is based on ring topology.
Arnet
It is based on the star or star topology distributed, but has a topology and protocol.
6. Network devices
NIC / MAU (Network Card) "Network Interface Card (network interface card) or" Medium Access Unit (Medium Access Unit). Each computer needs the hardware to transmit and receive information. This is the device that connects other computer network computadorau with the physical environment. The NIC is a type of expansion card from the computer and provides a port on the back of the PC to which it connects the network cable. Today more and more computers with network interface, primarily Ethernet incorporated. It is sometimes also necessary network card, a transceiver. This is a device that connects to the physical environment and the card, either because it is not possible direct connection (10 base 5) or because the medium is different from that to the card.
Hubs (concentrators)
These are computers that allow structured cabling networks. The variety of types and characteristics of these teams is great. At first there were only wiring hubs, but have increasingly greater number of network capacity, remote management, etc. The trend is to incorporate more functions in the hub. There are hubs for all types of physical media.
Repeaters
Teams are physically active. Prolong the length of the network by joining two segments and amplifying the signal, but with it also amplify the noise. The network remains a single, which still apply the limitations on the number of stations that can share the medium.
"Bridges" (Bridges)
Are teams joining two networks operating on low-level protocols at the level of media access control. Only network traffic that is directed to the other through the device. This allows administrators to divide the networks into logical segments, relieving traffic interconnections. Bridges produce signals, thus noise is not transmitted through them.
Routers (Router)
They are networking equipment operating at the level of network protocols. Can use different interconnection systems improve the efficiency of transmission between networks. Its operation is slower than bridges but its capacity is greater. Allow even link two networks based on a protocol by one using a different protocol.
"Gateways"
Teams are to interconnect networks with completely different protocols and architectures at all levels of communication. The translation of the information units greatly reduces the transmission rate through these devices.
Servers
These are computers that allow connection to the network of peripheral equipment for both input and output data for. These devices are offered in the network as shared resources. Thus a terminal connected to one of these devices can establish sessions against several multi-user computers available on the network. Similarly, any system on the network can print to printers connected to a server.
Modems
These are computers that enable computers to communicate with each other over telephone lines, modulation and demodulation of electronic signals that can be processed by computers. Modems can be external (communication device) or internal (internal communication device or circuit board that is inserted into an expansion slot of the computer).



















